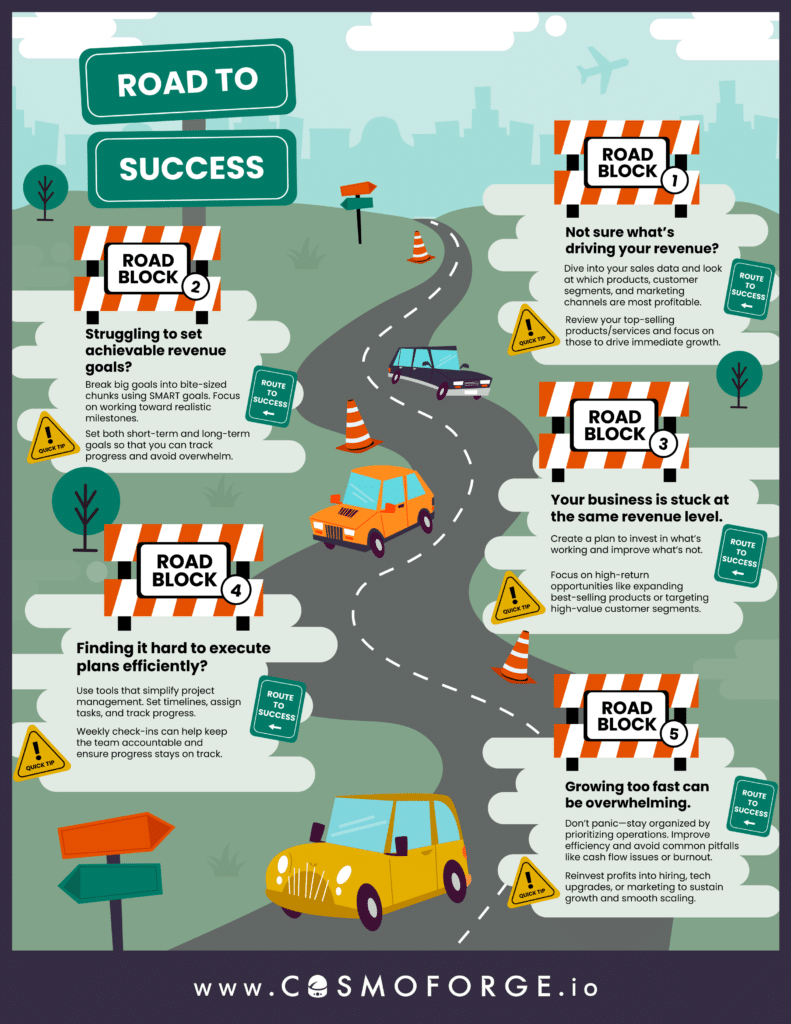
The $1M/Year Revenue Challenge
For many businesses, breaking the $1M revenue barrier is more than just a financial milestone—it’s a validation of the business model, a signal that the company is on the path to sustainable growth. However, this figure can also become a psychological barrier, creating a sense of an invisible ceiling that seems difficult to break through. It’s important to understand that this isn’t just about hitting a specific number; the strategies and challenges discussed here apply to any significant revenue push, whether your goal is $1 million, $10 million, or beyond.
The challenges in reaching this milestone are often both psychological and operational. Psychologically, the fear of scaling too quickly or the anxiety of maintaining growth can create a sense of paralysis. Operationally, businesses often face bottlenecks in processes, customer acquisition, or resource allocation that prevent them from scaling efficiently.
In today’s guide, we’ll break down the essential steps of a successful revenue growth campaign.
- Chapter 1: Analyzing Your Current Revenue
- Chapter 2: Setting Realistic Revenue Goals
- Chapter 3: Building a Roadmap to Success
- Chapter 4: Executing the Roadmap
- Chapter 5: Overcoming Common Obstacles
Chapter 1: Analyzing Your Current Revenue
Understanding the Drivers and Limits of Your Current Revenue
Breaking through revenue barriers requires a clear understanding of what drives your business’s income. Whether you’re running a small e-commerce site or a service-based business, you must identify the core elements contributing to your bottom line. These elements typically fall into three categories: products/services, customer segments, and marketing channels.
1. Identifying Key Revenue Drivers
To begin, analyze these three areas to determine where your revenue is coming from:
- Products/Services: Examine your product or service offerings to see which are performing well. Which products or services generate the most revenue? Are there any that are consistently underperforming? Understanding this will help you focus your resources on your most profitable offerings.
Actionable Steps:
- Review Sales Data: Pull sales reports from your CRM or accounting software. Rank your products or services by revenue contribution.
- Analyze Profit Margins: Beyond revenue, consider the profitability of each product or service. A high-revenue item might have a slim margin, meaning it’s less impactful on your bottom line than you think.
- Customer Feedback: Use surveys or direct feedback to understand why certain products/services are more popular. This can provide insight into market demand.
- Customer Segments: Different customer segments can have vastly different impacts on your revenue. Who are your most valuable customers? Are there segments that drive more repeat business or higher average order values?
Actionable Steps:- Segment Your Customers: Divide your customers into segments based on characteristics like purchase frequency, order size, or demographics.
- Calculate Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Determine which segments have the highest CLTV. Focus on nurturing these segments to maximize revenue.
- Personalize Marketing Efforts: Tailor your marketing efforts to the preferences and behaviors of your most valuable segments. This could mean different messaging, offers, or communication channels.
- Marketing Channels: Not all marketing channels contribute equally to your revenue. Some may drive high traffic but low conversions, while others might bring in fewer but more valuable customers.
Actionable Steps:
- Channel Performance Analysis: Use analytics tools to assess the performance of each marketing channel. Look at metrics like conversion rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and return on ad spend (ROAS).
- Focus on High-Performing Channels: Allocate more resources to the channels that provide the best ROI. Conversely, consider whether underperforming channels can be improved or if they should be cut.
Identify Your Revenue Bottlenecks
Once you’ve identified your key revenue drivers, the next step is to pinpoint bottlenecks that might be holding back your growth. A bottleneck is anything that restricts your business’s ability to generate more revenue, and it can occur at any point in your revenue drivers.
Common Bottlenecks to look out for:
- Low Returning Customer Rates: If you have a low rate of returning customers, your business is likely overly reliant on constantly acquiring new customers, which is typically more expensive than retaining existing ones.
Actionable Steps:- Track Repeat Purchase Rates: Monitor how often customers return to buy again. If the rate is low, consider implementing loyalty programs or personalized follow-up campaigns.
- Customer Feedback: Ask lapsed customers why they haven’t returned. Their insights can guide improvements in your offerings or customer service.
- High Churn Rates: In subscription-based or service businesses, a high churn rate (the percentage of customers who stop using your service) can severely limit growth.
Actionable Steps:- Monitor Churn Metrics: Calculate your monthly or yearly churn rate. A high churn rate may indicate problems with your product/service, onboarding process, or customer support.
- Conduct Exit Surveys: Reach out to customers who have churned to understand their reasons for leaving. Use this data to make necessary adjustments.
- Inefficient Sales Processes: If your sales cycle is too long or your conversion rates are low, your revenue potential is limited.
Actionable Steps:- Review Sales Funnel: Map out your entire sales process from lead generation to conversion. Identify any stages where prospects frequently drop off.
- Optimize Sales Training: Ensure your sales team is well-trained and equipped with the tools they need to close deals effectively. Consider automating parts of the process to reduce time and effort.
How to find your bottlenecks:
Identifying bottlenecks in your revenue drivers is critical, but what happens when the usual suspects—low returning customer rates, high churn rates, or inefficient sales processes—aren’t the issue? Sometimes, the bottleneck isn’t immediately obvious, and you need to start from scratch to find it. Here’s how to approach this situation systematically:
1. Conduct a Holistic Review of Your Business Operations
When the bottleneck isn’t clear, start by stepping back and conducting a thorough review of your entire business. Look at every aspect of your operations, from marketing to customer service, to find areas that might be limiting growth.
Actionable Steps:
- Map Out the Customer Journey: Document every touchpoint a customer has with your business, from the first interaction to post-purchase follow-ups. Look for areas where there’s friction or drop-off.
- Analyze Operational Efficiency: Review how your business operates day-to-day. Are there inefficiencies in how tasks are completed? For example, are there delays in product fulfillment, or are internal processes creating bottlenecks in service delivery?
- Evaluate Resource Allocation: Consider whether your resources (time, money, personnel) are being used effectively. Misallocation of resources can create bottlenecks, such as underfunding a marketing channel that could drive significant growth or overstaffing a department with little impact on revenue.
2. Gather Data and Seek Out Anomalies
When the bottleneck isn’t apparent, data can be your best friend. Dive deep into your business metrics to spot anomalies or patterns that might indicate a hidden issue.
Actionable Steps:
- Performance Metrics: Look at a broad range of metrics, including customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (LTV), website traffic, conversion rates, and product returns. Are there any metrics that stand out as unusual or inconsistent with your expectations?
- Segment Analysis: Break down your data into different segments, such as customer demographics, product categories, or geographic regions. Sometimes, the bottleneck is specific to a particular segment and might not be visible in aggregated data.
- Trend Identification: Compare current performance against historical data to spot trends. A sudden drop in website traffic from a particular source or a decline in average order value might signal an emerging bottleneck.
3. Conduct Qualitative Research
Quantitative data is essential, but sometimes the answers lie in qualitative insights. Talk to your customers, employees, and partners to gain a deeper understanding of where problems might be occurring.
Actionable Steps:
- Customer Interviews: Reach out to a sample of your customers to ask about their experience with your product or service. What challenges did they face? Why did they choose your business, and why might they hesitate to return?
- Employee Feedback: Your frontline employees often have the best insights into where operational bottlenecks exist. Regularly solicit feedback from your team to uncover hidden issues in your processes.
- Partner Insights: If you work with suppliers, distributors, or other partners, ask them about any challenges they face in working with you. A delay in supply chain or communication issues could be an overlooked bottleneck.
Case Study
Background: GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies is a small business that specializes in eco-friendly gardening tools and supplies. The company had experienced strong growth in its early years, largely due to the popularity of its flagship product, a biodegradable plant pot. However, in the past year, their revenue plateaued at around $850,000 annually, despite introducing new products and increasing their marketing budget. The owners, Sarah and Mark, were unsure why they couldn’t push beyond this revenue ceiling.
Step 1: Understanding the Drivers and Limits of Current Revenue
Sarah and Mark began by examining their key revenue drivers: products, customer segments, and marketing channels.
1. Identifying Key Revenue Drivers
- Products/Services: GreenLeaf’s product line had expanded to include organic fertilizers, gardening tools, and decorative planters. However, sales data revealed that the original biodegradable plant pot still accounted for 60% of their revenue. The newer products, despite being well-received by a niche audience, hadn’t gained significant traction.
Actionable Steps:- Review Sales Data: Sarah pulled reports from their accounting software and ranked their products by revenue contribution. The biodegradable plant pot was clearly the top performer, while other products lagged behind.
- Analyze Profit Margins: Mark analyzed the profitability of each product. Surprisingly, the organic fertilizers, although generating less revenue, had a higher profit margin than the plant pots. This indicated a potential area to focus on for improving overall profitability.
- Customer Feedback: To understand why the plant pot was so popular, they surveyed their customers. The feedback highlighted that customers valued the product’s environmental benefits and its unique design.
- Customer Segments: GreenLeaf’s customer base was diverse, ranging from urban gardeners to professional landscapers. Sarah segmented their customers based on purchase frequency and order size. The data revealed that urban gardeners, who made frequent small purchases, were their most valuable segment in terms of volume, but professional landscapers, though fewer in number, had a higher lifetime value (CLTV).
Actionable Steps:- Segment Your Customers: Sarah divided customers into segments: urban gardeners, suburban homeowners, and professional landscapers.
- Calculate CLTV: She calculated the CLTV for each segment, finding that professional landscapers, while a smaller group, were the most profitable due to larger, recurring orders.
- Personalize Marketing Efforts: Based on these insights, they tailored their marketing strategies. For urban gardeners, they focused on frequent promotions, while for landscapers, they offered bulk purchase discounts and personalized service.
- Marketing Channels: GreenLeaf had invested heavily in social media marketing, particularly on Instagram, which was popular among urban gardeners. However, their conversion rates from these channels were lower than expected. They had also dabbled in content marketing through a gardening blog, which drove significant traffic to their website but didn’t translate into many sales.
Actionable Steps:- Channel Performance Analysis: Using Google Analytics and social media insights, Mark assessed the performance of each marketing channel. Instagram drove the most traffic but had a low conversion rate, while the blog attracted highly engaged visitors who didn’t convert immediately.
- Focus on High-Performing Channels: They decided to enhance the blog’s content with more direct calls-to-action and product links, leveraging the engaged audience to drive conversions. Additionally, they explored email marketing to nurture relationships with the blog’s readers.
2. Identifying Revenue Bottlenecks
Despite having a good understanding of their revenue drivers, Sarah and Mark needed to pinpoint the bottlenecks preventing growth. They looked beyond the obvious issues like customer retention and churn, which were relatively healthy, and focused on more nuanced problems.
Common Bottlenecks to Look Out For:
- Low Returning Customer Rates: While GreenLeaf had a decent rate of returning customers, Sarah noticed that customers who bought the flagship product often didn’t purchase other items from the catalog. This indicated a missed opportunity for cross-selling.
Actionable Steps:- Track Repeat Purchase Rates: Sarah began closely monitoring how often customers who bought the plant pot returned to buy other products. She also implemented a loyalty program to encourage repeat purchases across the product range.
- Customer Feedback: Through follow-up surveys, they discovered that many customers were unaware of their broader product range. This insight led to more cross-promotional efforts in their marketing.
- Inefficient Sales Processes: Although the sales funnel seemed functional, Mark suspected there were inefficiencies, particularly in the way they managed bulk orders for professional landscapers. He mapped out the entire sales process, from inquiry to fulfillment, and identified delays in responding to large order inquiries, which sometimes led to lost sales.
Actionable Steps:- Review Sales Funnel: Mark mapped out the sales funnel and identified stages where landscapers frequently dropped off. Delays in quoting and processing large orders were a major issue.
- Optimize Sales Training: They streamlined the sales process by automating the quote generation for bulk orders and training the sales team to respond faster.
3. How to Find Your Bottlenecks
With the common bottlenecks addressed, Sarah and Mark took a deeper dive to ensure they hadn’t missed any hidden obstacles.
Conduct a Holistic Review of Business Operations
- Map Out the Customer Journey: They documented every touchpoint in the customer journey, from visiting the website to receiving the product. This revealed that the website’s product pages were informative but lacked persuasive elements like customer testimonials or clear value propositions, leading to lower-than-expected conversions.
Actionable Steps:- Analyze Operational Efficiency: Mark reviewed how GreenLeaf operated daily. He discovered that their inventory management system wasn’t synchronized with the website, leading to occasional stockouts and frustrated customers.
- Evaluate Resource Allocation: They realized that while they had invested heavily in social media, they had neglected email marketing, which could have been a powerful tool for engaging existing customers.
Gather Data and Seek Out Anomalies
- Performance Metrics: Sarah and Mark scrutinized a wide range of metrics. They noticed an anomaly: while overall website traffic was high, traffic from search engines had been steadily declining. This indicated potential issues with their SEO strategy.
Actionable Steps:- Segment Analysis: They broke down the data by source and discovered that referral traffic, particularly from gardening blogs and forums, had a higher conversion rate than paid ads on social media. This led them to shift some of their marketing budget towards influencer partnerships and guest blogging.
- Trend Identification: They compared current performance against historical data and spotted a worrying trend: the average order value (AOV) was decreasing. Customers were buying fewer items per transaction, possibly due to a lack of bundled offers or incentives.
Conduct Qualitative Research
Finally, they turned to qualitative insights to confirm their findings and uncover any additional bottlenecks.
- Customer Interviews: Sarah reached out to a sample of customers to discuss their shopping experiences. Several customers mentioned that they appreciated the product quality but found the website difficult to navigate, particularly when trying to browse related items.
Actionable Steps:- Employee Feedback: Mark gathered feedback from their customer service team, who reported frequent complaints about delayed deliveries, especially during peak gardening seasons. This prompted them to review and improve their supply chain management.
- Partner Insights: They also consulted with their shipping partner, who pointed out that the packaging for certain products was unnecessarily bulky, leading to higher shipping costs and slower delivery times.
Conclusion
By following these steps, GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies gained a comprehensive understanding of their current revenue drivers and identified several key bottlenecks that were holding them back. Among these, the most urgent revenue bottleneck was the inefficiency in their sales processes, particularly the delays in responding to large order inquiries from professional landscapers. This bottleneck was critical because it directly impacted their ability to close high-value sales, which could have significantly boosted their revenue.
While they hadn’t yet implemented all the changes, addressing this specific issue became their top priority. By streamlining the sales process and automating quote generation for bulk orders, GreenLeaf was positioned to capture more revenue from their most valuable customer segment. With this bottleneck on its way to being resolved, they were better equipped to push past the $1M revenue barrier and continue scaling their business.
Breakout Section: Gathering Data Without Much Past Data
For newer businesses or those with limited data history, collecting and analyzing data might seem challenging. However, it’s entirely possible to start building a solid data foundation that will inform your growth strategy.
Step-by-Step Guide on Starting Data Collection:
- Identify Key Metrics: Determine which metrics are most crucial for your business. These typically include customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), conversion rates, and churn rates. If you’re unsure where to start, focus on metrics that directly impact your revenue, like conversion rates or customer retention.
- Choose Simple Tools: You don’t need sophisticated software to start tracking data. Tools like Google Analytics for website data, basic CRM systems for sales tracking, and spreadsheets for manual data input can be highly effective. Use free versions of CRM tools like HubSpot or Zoho to start tracking customer interactions and sales without upfront costs.
- Set Up Data Tracking: Ensure that all critical touchpoints in your customer journey are being tracked. This might include website visits, email sign-ups, purchases, and customer service interactions. Use Google Tag Manager to set up tracking on your website without needing to modify the code directly.
- Establish Baselines: With even a few weeks or months of data, you can establish baselines for your key metrics. These baselines will serve as reference points to measure your performance over time. Regularly review your baselines to identify trends or shifts in performance, allowing you to make timely adjustments.
- Iterate and Improve: As your data set grows, continually refine your tracking methods and the metrics you monitor. Use the insights gained to make informed decisions about where to focus your growth efforts. Schedule monthly or quarterly reviews of your data to evaluate progress and adjust your strategies as needed.
Tools and Techniques for Small Businesses with Limited Data History:
- Google Analytics: Essential for tracking website performance and understanding visitor behavior. Set up goal tracking to measure conversions and other critical actions.
- CRM Systems: Implement a CRM to manage customer relationships, track sales, and analyze customer data. HubSpot and Zoho offer robust free versions.
- Surveys and Feedback: Collect qualitative data through customer surveys, feedback forms, and reviews. This can provide insights that quantitative data alone might not reveal, such as customer satisfaction and brand perception.
Chapter 2: Setting Realistic Revenue Goals
The Importance of Goal Setting
Setting realistic revenue goals is essential because it provides a clear direction and serves as a north star for your decision-making process. Unrealistic goals can lead to poor strategic choices, wasted resources, and frustration. On the other hand, setting overly simplistic goals might mean missing out on growth opportunities. A balanced, realistic goal enables your business to stretch its potential while remaining feasible within your current resources and capabilities.
Aligning revenue goals with your company’s vision is crucial. Your goals should not only aim for growth but also reflect your company’s broader objectives, whether that’s increasing customer loyalty, expanding into new markets, or enhancing operational efficiency. Without clear, attainable goals, decision-making can become erratic, and resources may be misallocated, stunting potential growth.
Creating SMART Goals
A proven framework for setting clear, actionable goals is the SMART system. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Let’s break down how to create effective revenue goals using this framework.
- Specific: Your revenue goal should be well-defined and focus on a particular aspect of your business, whether that’s increasing sales from a specific product line or improving repeat customer rates.
- Example: “Increase revenue from our biodegradable plant pots by 20% within the next quarter through targeted promotions and upselling.”
- Measurable: There must be a way to track progress. Define how you’ll measure the success of your goal.
- Example: “Track the increase in revenue from plant pots using weekly sales reports and analyze the impact of upselling through conversion rates.”
- Achievable: While ambitious goals are motivating, they must also be realistic given your current resources and market conditions. Setting unattainable goals can demoralize your team and waste time.
- Example: Instead of setting an overly ambitious goal like “Double revenue in 3 months,” aim for a steady increase, like “Achieve a 15% revenue increase in 6 months.”
- Relevant: Ensure your goals align with your company’s long-term vision and current market opportunities. They should be relevant to your specific business challenges.
- Example: “Focus on increasing sales of the eco-friendly plant pots, as this product aligns with our mission of promoting sustainable gardening practices.”
- Time-bound: Every goal should have a deadline. Without a clear timeframe, there’s no urgency to drive progress.
- Example: “Achieve this revenue increase by the end of the second quarter.”
Examples of Realistic vs. Unrealistic Revenue Goals:
- Realistic Goal: Increase overall revenue by 10% over the next six months by improving customer retention through loyalty programs and targeted email marketing.
- Unrealistic Goal: Triple overall revenue in 2 months without increasing marketing budget or adding new sales channels. This goal overlooks resource constraints and market realities.
Example: GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies
In Chapter 1, GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies identified a bottleneck in their bulk order sales process for professional landscapers. Armed with this insight, Sarah and Mark, the owners, decided to set a realistic revenue goal focused on improving their sales to this high-value customer segment.
GreenLeaf’s SMART Goal:
- Specific: Increase revenue from professional landscapers by 25% over the next two quarters by streamlining the sales process and offering bulk order discounts.
- Measurable: Track revenue from landscapers using the company’s CRM and set biweekly check-ins to monitor progress.
- Achievable: Based on past performance and recent improvements in the sales process, the team estimated that a 25% increase is both ambitious and achievable.
- Relevant: The goal aligns with GreenLeaf’s broader objective of growing their most profitable customer segment while maximizing their recent process improvements.
- Time-bound: The goal is set to be achieved within two quarters, providing a clear deadline.
By setting this SMART goal, Sarah and Mark ensured that their team would have a focused direction and actionable steps to work toward improving revenue from landscapers, rather than pursuing vague or unattainable objectives.
Breakout Section: Setting Goals with Limited Data
For businesses with limited historical data, setting goals can be challenging, but it’s still possible to set realistic targets using industry benchmarks, competitor analysis, and a cautious approach to forecasting.
Techniques for Forecasting Without Extensive Data:
- Use Industry Benchmarks: Look at standard growth rates for your industry and use them as a baseline for setting your own goals. For example, if eco-friendly gardening products typically grow at a rate of 5-10% per year, you can set a goal within this range.
- Leverage Competitor Analysis: Research competitors of similar size or product offerings to gauge how they are performing. Tools like SEMrush or industry reports can provide insights into their growth trends and help you set comparable goals.
- Test Small and Scale: If you’re unsure about how much growth to expect, start with a small, controlled experiment, like launching a marketing campaign on a single channel. Monitor the results, then scale up if the data shows positive trends.
Example from GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies: When GreenLeaf first introduced their new product line of organic fertilizers, they had limited data to forecast how well these products would perform. Instead of setting aggressive revenue goals, Sarah and Mark took a cautious approach:
- Industry Benchmark: Based on industry reports, they learned that organic fertilizers tend to grow at a modest rate of 6-8% annually.
- Competitor Analysis: Competitors with similar products showed steady but slow sales in the first year, with significant growth occurring only after targeted marketing efforts.
- Small Test: GreenLeaf set a goal to increase organic fertilizer sales by 5% over the next quarter, focusing on a small region with targeted promotions. After gathering data from this test, they adjusted their forecast and gradually scaled up their marketing efforts.
By using these forecasting techniques, businesses like GreenLeaf can set realistic goals that minimize risk while still providing a roadmap for growth.
Chapter 3: Building a Roadmap to Success
Now that you’ve identified where your business currently stands (Chapter 1) and set realistic goals (Chapter 2), it’s time to map out the path that will take you from your current position to your desired revenue targets. This chapter will guide you through the process of creating a strategic plan that aligns with your strengths, leverages growth opportunities, and weighs internal capabilities.
The goal is to think about what value your company provides, where your ideal customers are seeking that value, and how to create touchpoints that position you as the authority in solving their problems. Balancing this with your operational capacity ensures you’re creating a feasible and sustainable plan.
From Current Drivers to Your Revenue Goal
The roadmap to success starts by leveraging what you already know: the drivers behind your current revenue. Building on these strengths while identifying key growth opportunities will ensure that your strategy is both actionable and effective.
- Mapping Out a Strategic Plan That Builds on Existing Strengths
- Leverage Your Strengths: Start by reviewing the strengths identified in Chapter 1. What’s already working well in your business? Which products, customer segments, and channels are the most profitable?
Actionable Steps:- Focus on expanding relationships with high-value customer segments by improving specific processes, offering discounts, and building personalized experiences.
- Increase promotion of your top-performing products while introducing complementary offerings to increase average order value.
- Leverage Your Strengths: Start by reviewing the strengths identified in Chapter 1. What’s already working well in your business? Which products, customer segments, and channels are the most profitable?
- Identifying Key Opportunities for Growth and Improvement
- Once you’ve outlined your strengths, it’s time to look for opportunities to expand. Where are your customers looking for value, and how can you position your business to meet those needs more effectively?
Actionable Steps:- Increase Visibility in Relevant Channels: Identify the platforms, industry associations, or forums where your ideal customers spend time and establish your presence there.
- Create Micro-Value Opportunities: Offer content that educates your audience about the value you provide, such as blog posts, instructional videos, or downloadable guides that position your business as a thought leader.
- Bundle Products for Upselling: Create value-added product bundles to increase order sizes and make purchasing decisions easier for your customers.
- Once you’ve outlined your strengths, it’s time to look for opportunities to expand. Where are your customers looking for value, and how can you position your business to meet those needs more effectively?
Framework for Feasibility
While growth opportunities are exciting, they must be weighed against your internal capabilities. A roadmap is only as good as your ability to execute it, so assessing feasibility is crucial.
- Assess the Feasibility of New Initiatives
- Look critically at your company’s resources—financial, human, and operational—to determine what’s realistic. Can your current team handle the increased workload from new campaigns, partnerships, or product launches? Do you have the infrastructure to scale production or handle larger orders?
Actionable Steps:- Conduct a resource audit: What team members, tools, or systems need upgrading to support new initiatives?
- Consider automation or outsourcing options for areas like customer service or marketing, where the internal team may be stretched too thin.
- Set clear timelines and milestones to ensure that your initiatives are implemented gradually and effectively.
- Look critically at your company’s resources—financial, human, and operational—to determine what’s realistic. Can your current team handle the increased workload from new campaigns, partnerships, or product launches? Do you have the infrastructure to scale production or handle larger orders?
- Implementing Initiatives Within a Company
- For successful initiative implementation, alignment across teams is essential. Without this, even the best strategy can fall apart due to poor communication or lack of buy-in.
Actionable Steps:
- Cross-Department Alignment: Ensure that all relevant teams—marketing, sales, operations—are aligned on the same goals. Clear communication and shared objectives are essential for seamless execution.
- Create Clear Ownership: Assign clear roles and responsibilities for each step of the initiative. Ensure every person or team knows their role in the larger strategy.
- Regular Check-Ins: Schedule consistent reviews with department heads to ensure everyone is on track and to address any emerging challenges.
Opportunity Analysis
After identifying growth opportunities and confirming their feasibility, it’s time to evaluate their potential return on investment (ROI). Prioritizing opportunities based on impact and ease of execution will help you focus on what matters most.
- Tools for Evaluating the ROI of Potential Initiatives
- Use data-driven tools to assess the financial viability of new initiatives. ROI calculators, cost-benefit analysis models, and performance dashboards can help quantify the potential return from each opportunity.
Actionable Steps:- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Estimate the cost of implementing each initiative (e.g., new hires, marketing costs, product development) versus the potential revenue gain.
- Test and Learn: Pilot smaller-scale versions of new initiatives to gather data before making large investments. For example, run a small campaign to assess interest before scaling up.
- Utilize ROI Calculators: Compare upfront costs with expected returns to ensure initiatives are worth the investment.
- Use data-driven tools to assess the financial viability of new initiatives. ROI calculators, cost-benefit analysis models, and performance dashboards can help quantify the potential return from each opportunity.
- How to Prioritize Opportunities Based on Impact and Feasibility
- Not all opportunities should be pursued at once. Use a prioritization matrix to rank potential initiatives by impact and feasibility. Focus on the initiatives that will have the biggest payoff with the least amount of complexity to implement.
Actionable Steps:- High Impact, High Feasibility: These are your top priorities. They offer the most significant growth potential with minimal barriers to implementation.
- High Impact, Low Feasibility: These should be considered for long-term planning. They have high potential but require more resources or significant changes to execute.
- Low Impact, High Feasibility: These can be quick wins but won’t drive significant growth. Implement them as support initiatives to bolster other efforts.
- Not all opportunities should be pursued at once. Use a prioritization matrix to rank potential initiatives by impact and feasibility. Focus on the initiatives that will have the biggest payoff with the least amount of complexity to implement.
Example: GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies – Building a Roadmap to Success
Let’s return to the GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies business we discussed in Chapters 1 and 2. Now that Sarah and Mark have analyzed their revenue drivers and set a realistic goal (a 25% increase in revenue from professional landscapers within two quarters), they need to develop a roadmap that takes them from their current position to their target.
- Leverage Existing Strengths:
- GreenLeaf’s biodegradable plant pots are a top seller, and professional landscapers are a high-value customer segment. Their roadmap focuses on improving the bulk ordering process for landscapers and introducing bundled product packages (biodegradable pots with organic fertilizers) to increase average order value.
- Key Opportunities for Growth:
- Visibility in Niche Channels: Sarah and Mark identified that landscapers frequent industry-specific forums and attend trade shows. They plan to increase GreenLeaf’s presence in these spaces by sponsoring events and creating targeted content for these platforms.
- Creating Micro-Value: GreenLeaf will launch a series of blog posts and downloadable guides aimed at landscapers, focusing on sustainable gardening practices and the benefits of using eco-friendly products. This will position them as an authority in the industry while generating leads.
- Feasibility Assessment:
- GreenLeaf’s team is small, and while they can handle current operations, the increased focus on landscapers and content creation may stretch their capacity. After conducting a resource audit, they decide to outsource content creation to a freelance writer and bring in a part-time assistant to manage incoming landscaper orders.
- Timelines are set for each initiative, ensuring gradual implementation. The landscaper-focused marketing campaign will roll out over three months, with regular check-ins to adjust as needed.
- Opportunity Analysis and Prioritization:
- High Impact, High Feasibility: Streamlining the bulk ordering process is the highest priority. It’s a quick win with minimal costs and immediate benefits. This will be the first initiative to be fully executed.
- High Impact, Low Feasibility: Entering new channels, like attending trade shows, will have significant impact but requires more investment and planning. This is placed on a longer-term timeline.
- Low Impact, High Feasibility: Blogging and creating downloadable guides are low-cost, low-effort initiatives. They will be done concurrently with the bulk order improvements but won’t require as many resources.
By following this roadmap, GreenLeaf is on track to achieve its 25% revenue growth goal for landscapers. The roadmap ensures that Sarah and Mark are focusing their resources where they’ll have the most impact while staying within the company’s operational limits.
Chapter 4: Executing the Roadmap
Now that you’ve mapped out a strategic plan to achieve your revenue goals (Chapter 3), the next step is ensuring you execute it effectively. Without proper execution, even the best plans fall apart. This chapter focuses on how to manage the process of following through on your roadmap, using project management best practices, making data-driven decisions, and knowing when to seek outside help.
Project Management for Revenue Growth
Executing your roadmap successfully depends on strong project management. This means organizing your initiatives, allocating resources effectively, and maintaining a clear timeline to track progress.
- Organizing and Managing Projects Effectively
- Create Clear Task Lists: Break down each initiative from your roadmap into smaller, manageable tasks. Assign these tasks to specific individuals or teams, and provide clear instructions and deadlines. Use project management tools like Asana, Trello, or Monday.com to create detailed task lists for each initiative. Each task should have a clear owner, a deadline, and a priority level.
- Set Priorities: Not all initiatives need to be tackled simultaneously. Prioritize tasks based on their potential impact on your revenue and ease of implementation. Focus on high-impact, high-feasibility projects first. Use a simple prioritization matrix to evaluate which tasks should be done immediately and which can wait. For example, streamlining your sales process might take priority over a social media campaign.
- Set Milestones and Regular Check-Ins: Milestones provide a clear sense of progress and help keep your team accountable. Regular check-ins ensure that projects stay on track and any issues are addressed promptly. Break down your revenue goal into monthly or quarterly milestones. Schedule regular check-ins (weekly or biweekly) to discuss progress, identify roadblocks, and make adjustments if needed.
When to Hire an Agency vs. In-House Execution
As you execute your roadmap, you may encounter resource constraints that limit your ability to manage all initiatives in-house. Knowing when to outsource versus keeping tasks internal is key to maintaining efficiency and ensuring quality.
- Deciding Between Outsourcing and Internal Execution
- Evaluate Internal Capacity: Assess your team’s ability to handle the workload. If your team is already stretched thin, taking on additional projects might lower the quality of output or lead to burnout.
Actionable Step: Conduct a resource audit to evaluate bandwidth. If key team members are maxed out, it may be time to consider outsourcing specific tasks, like content creation, SEO, or paid ads management. - Specialized Skills: Some tasks require expertise that your in-house team may not have. For example, developing a robust PPC (pay-per-click) campaign or managing complex marketing analytics may require an agency’s specialized skills.
Actionable Step: If your internal team lacks the necessary expertise for specific initiatives, consider outsourcing to an agency that specializes in those areas. For example, an SEO agency may help improve your visibility faster than internal efforts.
- Evaluate Internal Capacity: Assess your team’s ability to handle the workload. If your team is already stretched thin, taking on additional projects might lower the quality of output or lead to burnout.
- Criteria for Selecting the Right Agency Partner
- Industry Experience: Look for an agency with experience in your specific industry. They should have a track record of success in projects similar to yours.
- Cost vs. ROI: Weigh the cost of hiring an agency against the expected return on investment (ROI). If an agency can drive more revenue than the cost of their services, they’re worth the investment.
- Cultural Fit: Ensure the agency understands your company’s values, mission, and vision. This ensures smoother collaboration and better alignment with your goals.
Actionable Step: Create a shortlist of agencies and evaluate them based on their portfolio, client testimonials, and the initial discovery process. Select an agency that demonstrates strong communication and clear, actionable strategies.
Data Review & Adjustment
Once your initiatives are in motion, continuous monitoring is crucial. Tracking progress ensures that you can make adjustments in real-time to optimize your efforts and stay on course.
- How to Monitor Progress
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Set KPIs for each initiative. For example, if you’re running a new marketing campaign, track conversion rates, lead generation, or customer acquisition costs.
Actionable Step: Use tools like Google Analytics, CRM dashboards, or social media analytics to track KPIs in real-time. Make sure you’re regularly reviewing these metrics and comparing them to your initial projections. - Set Regular Review Points: In addition to weekly check-ins, establish formal review points every month or quarter to assess overall performance and make strategic decisions about the direction of the project.
Actionable Step: Create a reporting structure where each team member presents their progress at a monthly meeting. This provides visibility into how each project is tracking toward the revenue goal and allows for adjustments.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Set KPIs for each initiative. For example, if you’re running a new marketing campaign, track conversion rates, lead generation, or customer acquisition costs.
- Adjusting Strategies Without Overreacting
- Don’t Overreact to Small Fluctuations: Small fluctuations in performance are normal, especially in marketing and sales. Avoid making drastic changes based on short-term data unless there’s a clear downward trend.
Actionable Step: When reviewing performance data, look for sustained trends rather than reacting to short-term dips. Set thresholds that trigger reviews (e.g., if conversion rates drop by more than 15% for three weeks). - Strategic Pivots vs. Tactical Adjustments: If you notice that an initiative isn’t delivering expected results, determine whether you need a strategic pivot or a smaller tactical adjustment. Strategic pivots involve changing the overall approach, while tactical adjustments refine specific elements.
Actionable Step: If you find that a new customer segment isn’t converting well, you might need a strategic pivot, such as targeting a different audience. If your ad copy isn’t resonating, you might just need a tactical adjustment like testing new messaging.
- Don’t Overreact to Small Fluctuations: Small fluctuations in performance are normal, especially in marketing and sales. Avoid making drastic changes based on short-term data unless there’s a clear downward trend.
Breakout: Strategic Pivots vs. Tactical Adjustments
Knowing the difference between a strategic pivot and a tactical adjustment is key to making the right changes at the right time.
Strategic Pivot
A strategic pivot involves a significant shift in direction. You’ll need to consider a pivot when your core strategy isn’t delivering the expected results and adjustments aren’t making an impact. This could mean changing your target market, altering your product offering, or redefining your business model.
When to Pivot:
- Your core customer segment is not converting as expected.
- Market conditions have shifted (e.g., new competitors, economic downturns).
- Fundamental changes in customer needs or behavior.
How to Pivot:
- Revisit your core business assumptions and ask if they still hold true.
- Analyze your data to identify new growth opportunities or customer segments.
- Communicate the pivot clearly to your team, ensuring alignment across departments.
Tactical Adjustment
A tactical adjustment is a smaller, targeted change that fine-tunes your existing strategy. You’ll make adjustments when the overall approach is sound but specific elements aren’t performing optimally.
When to Adjust:
- Campaigns or initiatives show short-term underperformance.
- Conversion rates are low, but customer interest or engagement remains high.
- Specific elements, like messaging or pricing, are causing friction.
How to Adjust:
- Conduct A/B tests on underperforming elements, such as ad copy or product pages.
- Optimize processes that may be slowing down execution (e.g., customer service response times or checkout flows).
- Gather feedback from customers or team members to identify pain points.
Key Insight:
Strategic pivots are major shifts and should be considered carefully, while tactical adjustments are precise, data-driven tweaks. Knowing which action to take—and when—can be the difference between salvaging a strategy or chasing the wrong goals.
Example: GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies – Executing the Roadmap
Let’s revisit GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies, where Sarah and Mark are working toward a 25% revenue increase from professional landscapers within two quarters. They’ve mapped out a roadmap (Chapter 3) focusing on improving the bulk ordering process and creating content that provides value to their landscaper clients. Now, they need to ensure successful execution.
- Organizing and Managing Projects:
- Task Lists and Priorities: Sarah and Mark use a project management tool to break down their initiatives. For example, improving the bulk ordering process is split into tasks like redesigning the order form, training staff on bulk orders, and implementing a new CRM feature for landscapers.
- Milestones: They set quarterly milestones, aiming for a 10% increase in revenue by the end of the first quarter and a full 25% by the second. Weekly check-ins ensure they stay on track.
- Outsourcing vs. In-House Execution:
- GreenLeaf decides to outsource content creation for their landscaper blog to a freelance writer, allowing Sarah to focus on streamlining the bulk ordering process in-house. They evaluate freelance writers based on experience in sustainable gardening and industry expertise, ensuring they find a good fit.
- Data Review & Adjustment:
- Sarah and Mark set KPIs like order volume from landscapers, average order value, and blog traffic. They use their CRM and Google Analytics to track these metrics. After two months, they notice that while order volume is up, average order value isn’t increasing as expected. Rather than overreacting, they make a tactical adjustment by offering a discount for bundled orders, which improves their numbers by the next review cycle.
By staying organized, making data-driven decisions, and knowing when to outsource, Sarah and Mark ensure their roadmap is executed smoothly and their revenue goals are on track.
Chapter 5: Overcoming Common Obstacles
As your business begins to grow, new challenges will emerge that could potentially derail your progress. These obstacles, often referred to as “growing pains,” are common, but with the right strategies, you can navigate through them while keeping your business on track. This chapter focuses on managing these challenges, maintaining customer satisfaction, and ensuring financial health as your company scales.
Dealing with Growing Pains
Operational challenges often accompany periods of growth, from scaling production to managing a larger customer base. These growing pains, if not addressed early, can result in inefficiencies, reduced customer satisfaction, and missed revenue opportunities.
- How to Manage the Operational Challenges that Come with Scaling
- Streamline Operations: As your company grows, you’ll need to optimize processes that were once manageable at a smaller scale. This might involve automating repetitive tasks, upgrading systems, or hiring additional staff to handle increased demand.
Actionable Step: Identify bottlenecks in your operations and explore automation tools or software that can improve workflow efficiency. For example, customer service inquiries may need a more robust CRM, or fulfillment may require an upgrade to inventory management software. - Standardize Procedures: Create documented standard operating procedures (SOPs) for key areas like customer service, production, and sales. This ensures consistency as your team expands, and it reduces the chances of errors.
Actionable Step: Begin by documenting the most critical processes that are customer-facing or impact revenue. Make sure everyone on the team follows the same procedure to maintain quality and efficiency.
- Streamline Operations: As your company grows, you’ll need to optimize processes that were once manageable at a smaller scale. This might involve automating repetitive tasks, upgrading systems, or hiring additional staff to handle increased demand.
- Tips for Maintaining Quality and Customer Satisfaction During Growth
- Hire for Culture and Skill: During rapid growth, it’s tempting to hire quickly to fill immediate needs. However, focusing on both skills and cultural fit is key to maintaining a strong team that can deliver consistent quality. Avoid hiring solely based on urgency; instead, hire for long-term fit.
Actionable Step: Implement a structured hiring process that includes skill assessments and cultural fit interviews. Be clear about your company’s values, and ensure new hires align with them. - Improve Customer Communication: Growth often leads to increased customer inquiries and orders, which can strain customer service. Ensure that your team is equipped to handle the increased volume while keeping response times and quality high.
Actionable Step: Set up automated customer service tools, like chatbots or email autoresponders, to address common inquiries. Use customer feedback loops to continuously improve your communication process.
- Hire for Culture and Skill: During rapid growth, it’s tempting to hire quickly to fill immediate needs. However, focusing on both skills and cultural fit is key to maintaining a strong team that can deliver consistent quality. Avoid hiring solely based on urgency; instead, hire for long-term fit.
Read More: 10 Most Common Marketing Mistakes
Financial Management
As your revenue increases, so do the complexities of managing cash flow, budgeting, and reinvestment. Proper financial management ensures that your business remains stable during periods of rapid growth and can sustain further expansion.
- Strategies for Managing Cash Flow During Periods of Rapid Growth
- Monitor Cash Flow Closely: Growing businesses often face cash flow challenges because expenses—such as increased payroll or larger inventory orders—grow faster than incoming revenue. Monitoring your cash flow consistently helps prevent shortfalls.
Actionable Step: Implement cash flow forecasting tools that help you project future cash needs. Use these forecasts to ensure you always have enough liquidity to cover operational costs and invest in growth opportunities. - Negotiate Better Terms with Suppliers: If you anticipate significant growth, reach out to suppliers and negotiate longer payment terms or discounts for bulk orders. This will help you better manage cash flow while meeting increased demand.
Actionable Step: Build relationships with suppliers and negotiate terms that align with your growth needs, such as extended payment windows or volume-based discounts.
- Monitor Cash Flow Closely: Growing businesses often face cash flow challenges because expenses—such as increased payroll or larger inventory orders—grow faster than incoming revenue. Monitoring your cash flow consistently helps prevent shortfalls.
- Importance of Reinvesting Profits into Growth Initiatives
- Prioritize Growth Investments: As your profits increase, you’ll need to reinvest strategically to fuel further expansion. This could mean upgrading technology, expanding marketing efforts, or hiring key staff.
Actionable Step: Allocate a percentage of your profits to reinvest in initiatives that support your revenue goals, such as improving operations, increasing your marketing reach, or launching new products. Set clear goals for each investment to measure ROI. - Create a Growth Budget: Reinvestment is important, but it needs to be balanced with maintaining enough cash reserves to handle unforeseen challenges. A growth budget ensures that you have enough resources to scale without overextending financially.
Actionable Step: Design a growth budget where a fixed portion of profits is set aside for reinvestment. Be sure to leave a buffer for cash flow stability, emergencies, or market downturns.
- Prioritize Growth Investments: As your profits increase, you’ll need to reinvest strategically to fuel further expansion. This could mean upgrading technology, expanding marketing efforts, or hiring key staff.
Breakout Section: Resilience & Adaptability
How to Stay Resilient in the Face of Setbacks
Growth rarely happens without setbacks. To stay resilient:
- Embrace Change: Understand that setbacks are a natural part of scaling a business. Adaptability is critical—be open to pivoting strategies or making course corrections when needed.
Actionable Step: When a setback occurs, pause to evaluate the situation objectively. Assess what went wrong, learn from it, and develop a plan to address the issue. Keep your team informed, maintaining a culture that embraces flexibility. - Keep a Long-Term Perspective: Short-term failures can feel overwhelming, but maintaining a long-term outlook helps you stay focused on the bigger picture. Each setback is an opportunity to improve and adjust your strategy for future growth.
Actionable Step: Regularly revisit your business goals and vision to keep your team aligned with the long-term objectives. This reduces the emotional toll of short-term setbacks.
The Role of Adaptability in Long-Term Success
- Be Willing to Evolve: Markets, customer preferences, and economic conditions change, and businesses must evolve with them. Companies that are adaptable can pivot faster when opportunities or threats arise, ensuring long-term success.
Actionable Step: Foster a culture of adaptability within your team by encouraging experimentation and innovation. Regularly review market trends, customer feedback, and internal processes to identify areas where adjustments can be made.
Example: GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies – Overcoming Common Obstacles
As GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies scales to meet their revenue goals, Sarah and Mark begin to encounter some of the common obstacles associated with rapid growth.
- Managing Operational Challenges:
- As bulk orders from landscapers increased, GreenLeaf’s small team struggled to keep up with fulfillment. Sarah implemented an inventory management system to streamline stock tracking and fulfillment. Additionally, they hired a part-time warehouse worker to handle packaging and dispatch.
- To maintain quality customer service during growth, they integrated a CRM with automated responses for common inquiries, ensuring landscapers received timely updates on their orders without overwhelming the customer service team.
- Financial Management During Growth:
- With increased orders came the challenge of managing cash flow. Mark negotiated longer payment terms with their largest suppliers, giving GreenLeaf the flexibility to meet growing demand without stretching their finances too thin.
- They also reinvested a portion of their profits into upgrading their website’s bulk ordering feature and increasing marketing efforts to reach more landscapers, while still keeping enough cash on hand for unexpected expenses.
- Resilience & Adaptability:
- A sudden supply chain issue delayed the delivery of biodegradable pots, leading to backorders. Instead of panicking, Sarah and Mark communicated transparently with their landscapers, offering them discounts on future orders as compensation for the delay. This proactive approach not only solved the immediate problem but strengthened customer loyalty.
- To adapt, GreenLeaf also began sourcing alternative suppliers to ensure future stability, demonstrating their commitment to adaptability and resilience in the face of challenges.
By strategically managing growth obstacles and staying adaptable, Sarah and Mark positioned GreenLeaf Gardening Supplies for sustained, long-term success as they scaled the business.
Conclusion
Breaking through the $1M revenue barrier—or any significant revenue milestone—requires a structured approach. It’s not just about setting ambitious goals, but understanding your current revenue drivers, setting realistic and attainable objectives, building a strategic roadmap, executing that plan efficiently, and overcoming inevitable challenges along the way.
As you scale, growing pains will emerge, and it’s essential to manage operations, maintain customer satisfaction, and ensure financial stability. Staying adaptable and resilient, learning from setbacks, and reinvesting in key areas will keep your business on a sustainable growth path. By following these steps, you can break through your revenue barriers and position your business for long-term success.



