Welcome to the world of Pipedrive, your new secret weapon in the realm of customer relationship management (CRM) and sales tracking! If you’re diving into Pipedrive for the first time, you’re probably excited about the promise of streamlined sales processes and enhanced team productivity. This blog post is here to ensure that you kick things off on the right foot. We’ll guide you through setting up your Pipedrive system effectively, ensuring you know how to make the most out of its robust features from day one.
Curious about Pipedrive? Get an extended 30-day free trial here.
Understanding Pipedrive’s Capabilities and Limitations
Overview of Pipedrive Features
Pipedrive shines as a CRM tool because it’s designed by salespeople, for salespeople. At its core, Pipedrive excels at managing your contacts, tracking your deals through every stage of the sales funnel, scheduling activities to keep you on top of your tasks, and generating insightful reports that help you make data-driven decisions. Whether you’re a small team looking to grow or a larger enterprise aiming to streamline your sales operations, Pipedrive offers a flexible platform to support your sales journey.
Common Limitations and How to Overcome Them
No tool is perfect, and while Pipedrive offers a lot, there are a few areas where you might find yourself needing a bit more. For instance, while Pipedrive integrates well with many tools, you might find its native integrations lacking for some of your specific needs. Similarly, the platform has certain restrictions on custom fields, which can be a hiccup if you’re looking to capture very unique data points.
But worry not—most of these limitations can be effectively managed with a little creativity and the right third-party tools or add-ons. For deeper integration needs, tools like Zapier can connect Pipedrive with other platforms that aren’t supported natively, expanding your CRM’s functionality. Meanwhile, exploring the Pipedrive Marketplace will reveal a host of add-ons that can help you tailor the system to your precise requirements, from custom field enhancements to specialized reporting tools.
In the next sections, we’ll delve deeper into how you can map out your customer journey within Pipedrive and customize your setup to perfectly match your business’s workflow. Stay tuned to turn these insights into action and truly make Pipedrive your own!
Curious about Pipedrive? Get an extended 30-day free trial here.
Mapping Your Customer Journey
When configuring Pipedrive, or any CRM system, establishing a well-defined customer journey from the outset is critical. This foundational step is akin to setting the groundwork before laying bricks—it’s crucial for ensuring that all subsequent configurations and customizations fit perfectly and serve their intended purpose.
Defining Key Stages
Regardless of your industry, defining the stages of your customer journey—Contact, Lead, and Deal—is essential. These definitions should be tailored to how interactions typically unfold in your specific business context.
Key Definitions:
Contact: A contact is anyone who has entered your business’s orbit but hasn’t yet shown explicit interest in purchasing. This could be someone who signed up for your newsletter, attended a webinar, or simply handed you their business card at a networking event.
Lead: A lead is a contact who has shown specific interest in your product or service. This interest could be demonstrated by actions like requesting more information, asking for a product demo, or inquiring about prices. Leads are considered potential customers who might be nurtured towards making a purchase.
Deal: A deal represents a lead that has moved further down the sales pipeline and is actively engaging in discussions or negotiations that could lead to a sale. This stage involves concrete actions towards closing a sale, such as drafting a proposal, negotiating terms, or agreeing on the service or product specifics.
Example:
- Contact: This might be someone who submits a form on your website or signs up for an email newsletter.
- Lead: Someone who engages further, perhaps through inbound or outbound phone calls or email follow-ups.
- Deal: A lead that moves forward by requesting a quote or discussing project details, showing readiness to close.
Channel and Interaction Planning
Understanding the specific ways in which customers engage with your business across various channels is crucial for setting up a CRM like Pipedrive effectively. By thoroughly mapping out these engagement methods—whether they occur via email, social media, phone calls, or in-person meetings—you can tailor the CRM to capture and respond to these interactions accurately and efficiently. Tools like Miro can be exceptionally useful for visualizing these customer engagement pathways, allowing you to clearly see and plan for each touchpoint. This ensures that your CRM setup is not only comprehensive but also closely aligned with your customers’ journey, enhancing both customer experience and your team’s ability to manage relationships effectively.
We like to use Miro to help visualize this for future steps, but you can use any tool.
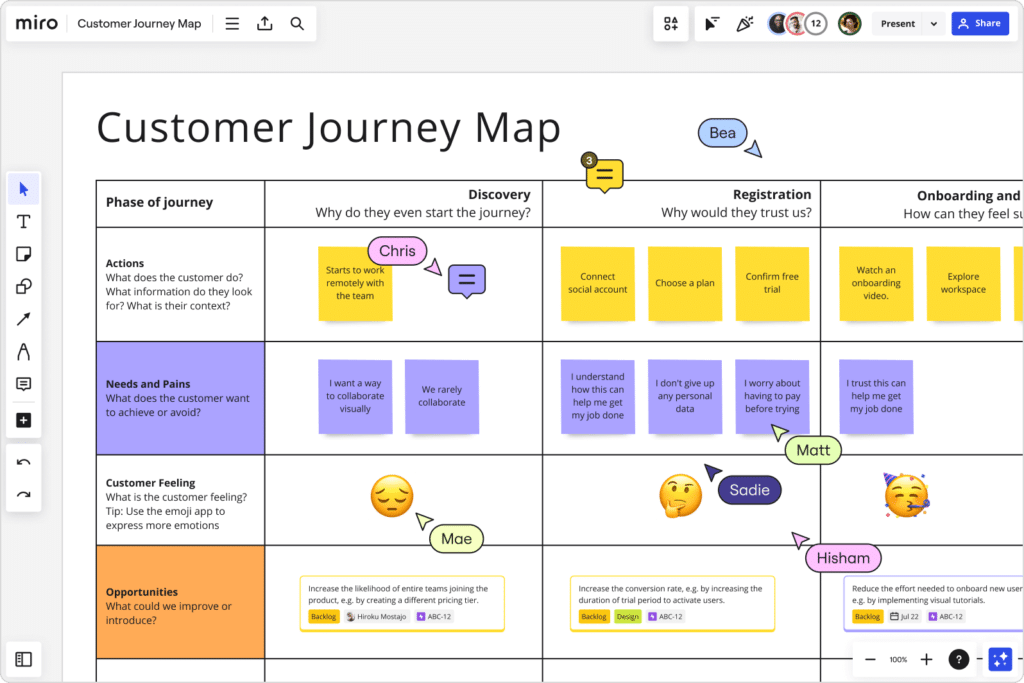
Example (Commercial Fence Contractor):
- Channels: These could include web forms, email communications, and phone calls.
- Interactions: From submitting a form for more information or signing up for a newsletter to making phone inquiries about services.
Integration Checklist for Seamless Engagement Tracking
Creating an integration checklist ensures that every customer touchpoint is captured and efficiently managed within Pipedrive. This checklist should be highly customized to fit the specific ways customers interact with your business. Once the checklist is complete, you know what needs to be built in Pipedrive.
Example:
- Form Submission Integration: Automatically log form submissions as new contacts or leads.
- Email Newsletter Integration: Track newsletter sign-ups and interactions.
- Phone Call Tracking: Record details of phone calls, updating statuses based on these interactions.
- Web Tracking Tools: Monitor interactions with critical website pages like quote requests or service descriptions.
This strategic approach to planning integrations is not just for one specific industry but is applicable across various sectors. Whether you’re a retail store, a software company, or a service provider, tailoring Pipedrive to closely match how your customers actually interact with your business maximizes both system efficiency and customer relationship management. By starting with this detailed mapping and integration plan, you ensure that your CRM system evolves with your business needs, providing a solid foundation that enhances operational workflows and customer satisfaction.
Curious about Pipedrive? Get an extended 30-day free trial here.
Customizing Your Pipedrive Environment
Now that you know the key stages of your customer journey that Pipedrive will need to cover, it’s time to fill in the details to make it all possible.
Define Your Pipeline Stages and Triggers
It’s essential to define clear pipeline stages and the specific triggers that move a prospect from one stage to the next. We recommend segments that are mutually exclusive but collectively exhaustive.
This approach ensures that every customer interaction is classified into a clearly defined category without any overlap, while simultaneously covering all possible scenarios of the customer journey.
Mutually exclusive stages mean that each stage is distinct with no ambiguity between them. For example, a lead cannot be both a ‘New Lead’ and an ‘Engaged Lead’ at the same time. This clarity is crucial for maintaining organized and understandable data, allowing for precise targeting and personalization of marketing and sales efforts. It prevents confusion and ensures that each team member knows exactly how to handle an interaction at each stage.
Completely exhaustive stages ensure that there are no gaps in your pipeline; every potential customer interaction or status is accounted for. This inclusivity is important to ensure that no customer falls through the cracks. Whether a contact is just beginning to show interest or is on the verge of closing a deal, the CRM system should have a predefined stage to capture and address their current status.
Applying this best practice enables more accurate reporting, better forecasting, and more efficient resource allocation. It allows businesses to automate processes confidently, knowing that the automation logic is based on well-defined and comprehensive stages, reducing errors and enhancing the effectiveness of the CRM system.
Example:
- Contact: Any individual who downloads a white paper or signs up for a webinar.
- Lead: A contact who has engaged further by requesting a demo or a detailed product consultation.
- Deal: A lead that sends a formal request for proposal (RFP) or engages in negotiation discussions.
Triggers for Stage Advancement:
- Moving from Contact to Lead might be triggered by the user scheduling a demo.
- Advancement from Lead to Deal could be initiated when the user submits an RFP.
Setting Up Custom Fields
When setting up custom fields in Pipedrive, a best practice across any industry is to focus on fields that directly support your sales process and decision-making. Typically, these include fields for tracking lead source, customer segmentation attributes (like industry type or company size), and key dates (such as follow-up tasks or contract expiration). A good rule of thumb is to ensure that each custom field provides clear value and actionable insights, avoiding any fields that clutter the system or duplicate existing data. This approach keeps your CRM lean and purposeful, enhancing usability and efficiency.
Example Checklist:
- Custom Fields:
- Lead Source (e.g., Webinar, White Paper, Referral)
- Demo Scheduled Date
- RFP Submission Date
- Projected Deal Value
- Expected Close Date
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation in Pipedrive is crucial for enhancing efficiency and ensuring consistency in handling repetitive tasks. When setting up workflow automations, start by identifying tasks that are performed frequently and are standard across similar processes. Common candidates for automation include lead follow-up emails after initial contact, setting reminders for follow-up calls a few days after a proposal has been sent, and alerting team members when a deal moves to a new stage.
To maximize the impact of automation, ensure that these workflows are connected to specific triggers in your CRM, such as the completion of a previous task or a change in deal status. This setup minimizes the need for manual intervention, reduces the likelihood of human error, and ensures timely action on critical tasks. Additionally, use conditional logic in automations to tailor responses based on customer data or interaction history, which can provide a more personalized experience for the client.
Lastly, regularly review and refine your automations. As business processes evolve and new insights are gained, adjustments might be necessary to maintain alignment with your operational goals. Implementing feedback mechanisms, such as surveys or user activity logs, can help identify which automations are performing well and which need improvement, ensuring your workflows remain efficient and effective.
Example Automations:
- Alerts for Follow-up: Set reminders for sales reps to follow up two days after a demo has been conducted.
- Move to Negotiation Stage: Automatically update the deal stage when an RFP is received.
- Lead Nurturing Emails: Trigger personalized emails based on the lead source or interest shown in specific products.
User Roles and Permissions
Defining user roles and setting permissions is crucial for protecting sensitive information and ensuring that team members have access to the tools and data they need to perform their roles effectively.
Example User Roles for a Technology Service Provider:
- Sales Representative: Access to lead and deal information, ability to update stages, but restricted from viewing financial forecasts and high-level analytics.
- Sales Manager: Full access to all sales data, including analytics, forecasts, and performance reports of team members.
- Marketing Specialist: Access to contact and lead information for campaign purposes, but no access to deal stages or financial details.
By customizing your Pipedrive environment using these specific strategies, you not only create a system that closely aligns with your business processes but also enhance your team’s ability to engage with prospects and customers more effectively. This targeted customization ensures that your CRM system supports your business goals, making it a powerful tool for driving sales and improving customer relationships.
Integrating with Other Tools
Once you’ve identified and prioritized your needs for Pipedrive, integrating it with other essential tools is the next critical step. These integrations enhance Pipedrive’s functionality and ensure seamless operation across different aspects of your business.
When implementing integrations in Pipedrive, prioritizing them based on their urgency and impact on your operations is essential. Start by categorizing potential integrations into high, medium, and low priority buckets, ensuring that each integration serves a specific, identifiable business purpose and isn’t just added for the sake of complexity.
High Priority Integrations should include those that are critical to your core operations. For example, if immediate response times are crucial for customer satisfaction in your industry, integrating your CRM with real-time communication tools like live chat or instant messaging platforms should be a top priority. Similarly, integrating with your email platform can be essential for ensuring all communications are captured and accessible in the CRM system, supporting seamless customer interactions and internal accountability.
Medium Priority Integrations might include connections with marketing automation platforms or advanced analytics tools. These are important for nurturing leads and making data-driven decisions but can be phased in once the most critical integrations are stable and operational. This approach ensures that your team isn’t overwhelmed with too many new tools at once and can focus on leveraging the most essential features effectively.
Low Priority Integrations could include nice-to-have but not essential tools, such as integrating with secondary social media platforms or specialized reporting tools that enhance but are not critical to day-to-day operations. These can be scheduled for later phases, allowing your team to adapt to the CRM’s core functionalities first.
Example:
- High Priority (Immediate):
- E-commerce Platform Integration: Automatically sync new orders as Deals in Pipedrive to track sales efficiently.
- Email Integration: Ensure that communication with customers is logged for follow-up and service excellence.
- Medium Priority (Short-term):
- Inventory Management System: Connect to monitor stock levels and link sales data to inventory changes.
- Low Priority (Long-term):
- Customer Feedback Tool: Integrate a system to gather customer reviews, which can later influence product development and marketing strategies.
Using Zapier to Extend Functionality
Zapier acts as a bridge to connect Pipedrive with other apps that do not have native integration. By automating workflows between Pipedrive and these external apps, you can streamline operations and reduce manual input.
Real-Life Example:
- Automating Lead Capture from Social Media Ads to Pipedrive:
- Use Zapier to create a workflow where new leads captured through Facebook Ads are automatically added to Pipedrive as contacts. Set up a Zap to capture lead details (name, email, interest) and funnel them directly into your CRM, tagging them for follow-up.
Data Import and Management
Managing the data that feeds into Pipedrive is just as important as setting up the system itself. Proper data management ensures that your CRM operates smoothly and provides reliable insights.
Preparing Your Data for Import
Before importing data into Pipedrive, it’s essential to ensure that it is clean and organized. This process prevents issues such as duplicates, incomplete entries, and inaccuracies.
Steps to Prepare Data:
- Data Cleaning:
- Consolidate data from different sources (e.g., old CRM, spreadsheets).
- Remove duplicates and correct inconsistencies.
- Verify and update contact details, like emails and phone numbers.
- Data Organization:
- Categorize data based on the customer journey stages defined in Pipedrive.
- Label data with tags for segmentation, such as customer type or lead source.
Maintaining Data Integrity
Continual management of data integrity is crucial for the ongoing effectiveness of your CRM.
Strategies for Data Management:
- Regular Data Audits:
- Schedule monthly reviews of data quality, looking for inaccuracies or incomplete records.
- User Training:
- Train team members on the importance of data hygiene and correct procedures for entering and updating data in Pipedrive.
- Automated Data Checks:
- Use tools or Pipedrive features to automate checks for duplicates or incomplete entries.
Training Your Team
Effectively training your team on Pipedrive ensures that they can leverage all its capabilities to enhance productivity and streamline sales processes.
Effective Training Techniques:
- Interactive Workshops: Organize regular training sessions using platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams where team members can interactively learn through real-time demonstrations and hands-on exercises.
- E-Learning Modules: Use tools like TalentLMS or Teachable to create structured, self-paced online courses that cover various aspects of Pipedrive, from basic functionalities to advanced features.
- Role-Based Training: Tailor training sessions according to the specific needs of different roles within your team. Sales representatives might need deep knowledge of deal tracking and mobile app usage, whereas managers might focus on reports and dashboard customization.
Creating Supportive Documentation:

- Comprehensive User Manuals: Develop detailed user manuals that include screenshots and step-by-step instructions. Tools like Google Docs or Confluence are ideal for creating and maintaining easily accessible online documentation.
- FAQ Sections: Compile a list of frequently asked questions that new users commonly encounter. This can be hosted on an internal wiki or a tool like Notion, where updates are straightforward and collaborative.
- Video Tutorials: Create video guides using tools like Camtasia or Loom for visual learners. These videos can demonstrate common tasks within Pipedrive and offer troubleshooting tips.
Monitoring and Optimizing Performance
Regular monitoring and continuous improvement of your Pipedrive setup will ensure it remains aligned with your business goals and adapts to changing business needs.
Setting Up Dashboards and Reports:
- Custom Dashboards: Utilize Pipedrive’s dashboard feature to create visual representations of sales metrics. Tools like Klipfolio or Pipedrive’s own Insights can help you integrate data from multiple sources and display key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most to your team.
- Regular Reporting: Schedule automatic reports to be generated and distributed among the team. Use Pipedrive’s reporting tools to assess metrics such as sales conversion rates, average deal size, and lead response time.
Continuous Improvement:
- Define Key Metrics: Establish a key metric that will guide adjustments. For sales teams, a critical metric might be the “lead-to-close ratio,” which helps understand the efficiency of the sales pipeline.
- Feedback Loops: Implement regular feedback sessions where team members can discuss challenges and suggest improvements to the Pipedrive setup. This could be structured around quarterly reviews using tools like SurveyMonkey to gather systematic feedback.
- Iterative Updates: Adopt an agile approach to CRM management, where you continuously refine and optimize workflows, fields, and integrations in Pipedrive. Tools like Trello or Asana can be used to manage these updates as individual projects or tasks.
- A/B Testing: Occasionally test different sales strategies or features within Pipedrive to see which works best. For example, trying different email templates linked via Pipedrive’s Email Integration to determine which yields a higher response rate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively setting up and optimizing Pipedrive is a dynamic and ongoing process that can significantly enhance your business’s operational efficiency and sales performance. By prioritizing feature setup and integrations, meticulously managing data import and integrity, training your team thoroughly with tailored content and interactive tools, and continuously monitoring and refining your CRM strategies through specific frameworks and key metrics, you lay a strong foundation for success. Each of these steps, when approached with attention to detail and strategic foresight, ensures that Pipedrive not only meets your current needs but also adapts to your evolving business landscape, driving growth and improving customer relationships. Embrace these practices to make the most out of Pipedrive and turn your CRM system into a powerful asset for your business.




